fluid mixed composition of phospholipid
Adhesion Proteins
proteins that are embedded in the plasma membrane
allow substances to move from one cell to another
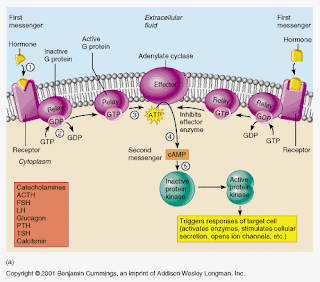
Receptor Proteins
combine with extracellular substances
Recognition Proteins
recognize what can enter or not enter the cell
Passive Transporters
have channels in their interior, no needs input of energyActive Transporters
transporters that need input of energy and move against the core gradient
Concentration Gradient
is a difference in the number per unit volume of molecules
Diffusion
is the name for the net movement of like molecules or ions
Electric Gradient
is simply a difference in electric charge between adjoining regions
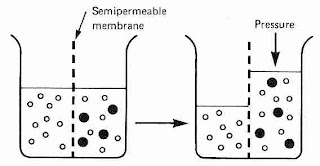
Pressure Gradient
pressure exerted per unit volume between two adjoining regionsOsmosis
is the diffusion of water across a selesctively permeable membrane
Hypotonic Solution
is the solution with fewer solutesHypertonic Solution
solution with more than one solutes
Isotonic Solution
solution that show no net osmotic movement
Hydrostatic Pressure
turger pressure
Osmotic Pressure
measure of the tendency of water to follow its water concentration
Endocytasis
a small patch of plasma membrane inside the cytoplasm
Exocytasis
a vesicles moves to the cell surface
Phagocytosis
cell eating. Is a common endocytic pathway